Atlas
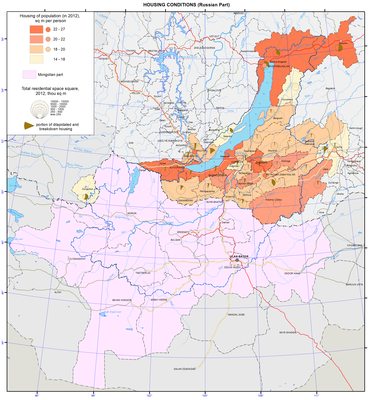
Housing conditions map
Housing
The most important indicator of the quality of modern life is the character of living conditions (“roof over head”), which combines a specific indicator of housing supply and an especially important from the ecological standpoint specific indicator of the meterage of old and dilapidated housing. The main information resources used for calculations included the data of the territorial bodies of the Federal State Statistics Service of Irkutsk oblast, the Republics of Buryatia and Tuva, and Zabaikalsky krai, as well as online resources.
Spatial differences in the living conditions in the low-level administrative divisions (district municipalities) and urban settlements (urban municipalities) are represented by: a) a total indicator and b) a specific per capita (m²/person) indicator. According to Russian definitions, a housing fund is a collection of all housing properties regardless of the forms of ownership including residential properties, special properties (hostels, shelters, temporary public housing, nursery homes for lonely seniors, orphanages, boarding homes for persons with disabilities and veterans, and boarding schools), apartments, residential properties of businesses, and other residential properties in buildings suitable for residence. Meanwhile, the housing fund does not include residential properties of the cottage-recreational complex, i.e. summer cottages, sports and tourist facilities, rest homes and other. It should be noted that the total area of residential buildings does not include communal space (stairwells, elevator lobbies, common corridors, lobbies and other), as well as non-residential space occupied by any institutions.
The background of the map is the per capita housing supply in administrative districts and cities. The cartogram shows a specific provision of the population with housing in district municipalities and urban entities. This rate for all four subjects of Russia in the basin is much lower than both the Russian and Siberian Federal District (SFD) averages (23.4 m²/person and 22.1 m²/person, respectively).
Spatial differences in the region according to this indicator of housing conditions are quite sharp (a two-fold difference between the minimum and maximum values – 14.1 and 29.9 m²/person (in the Tere-Khol district of the Republic of Tuva and the Zaigraevsky district in the Republic of Buryatia, respectively). Among urban settlements, Petrovsk-Zabaikalsky has the highest per capita rate of housing provision – 23.4 m²/pers., which equals to the average Russian indicators (2012), while the outsider is Chita (19.9 m²/person).
In terms of specific housing supply, all district and urban entities in the region are divided into four groups taking into account the average index for the SFD ( 22.1 m²/person). The category of high-status areas (Group 1 with more than 22.1 m²/person) includes slightly over 20% of the total number of territories. Thus, almost 4/5 of municipalities of the district and city levels in the Baikal basin belong to the areas, where a specific housing supply indicator is lower than the average for the SFD.
The housing fund in the Baikal basin is 46.8 million m² (2012). More than two fifths of it belong to the Republic of Buryatia (41.3 %), about two fifths to the Irkutsk oblast (37.5%), and more than one fifth to the Zabaikalsky krai (21.5%), while the contribution of Tuva is only 0.1%. The urban sector predominates – more than 3/4 (75. 8%). In the Baikal basin’s regions, this picture is highly contrasting: in Irkutsk oblast the share of the urban housing fund exceeds 9/10 (90.7%), while in the neighboring Republic of Buryatia it is less than 2/3 (59.8%).
The share of old and dilapidated housing is an indicative negative indicator of the quality of the housing fund. It represents a total share of more than 5% (this indicator has increased manifold in comparison with 1990).
References
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Housing and utilities of Zabaikalsky krai. Chita: Zabaikalkraistat. p 112.
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Housing and utilities of Irkutsk oblast in 2012. Irkutsk: Irkutskstat. p 76.
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Housing of the Republic of Buryatia. Ulan-Ude: Buryatstat. p 35.
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Districts of the Republic of Buryatia. Ulan-Ude: Buryatstat. p 102.
Federal State Statistics Service. Database of municipal indicators. Retrieved from http://www.gks.ru/dbscripts/munst/munst.htm
Document Actions
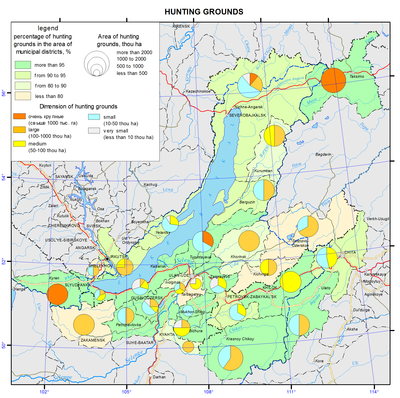
Hunting grounds map
Game animals
The resource potential of game animals of the Baikal basin has long been characterized by the abundance and high species diversity. This is due to the location of the territory at the intersection of Central-Asian, European-Siberian and East-Asian faunas, where representatives of all of these complexes, including species valuable for hunting, are found. Within the region, there are four typological landscape complexes, corresponding to the zonal and regional landscape subdivisions, namely: mountain-taiga, goletz, forest-steppe, and steppe. Each of them is characterized by a set of habitat types, the quality and quantity of which influence the number of animals.
The wildlife of the mountain taiga is the richest and most diverse; there manifestations of latitudinal zonality in the distribution of vegetation are complicated by the features of altitudinal zonality of its location in the mountains depending on the steepness and exposure of slopes. This creates prerequisites to spread the spectrum of landscape-ecological diversity of the conditions of animal habitats, and possibilities for most of them to choose the most valuable biotopes and, eventually, to increase in the number. In the mountain taiga squirrel, hazel grouse, sable, bear, and in some places musk deer are numerous. Siberian stag and roe deer inhabiting light slopes, forest openings and woodlots, as well as elk, inhabiting waterlogged intermountain depressions, creek valleys and wide plots of terraces in the coastal area of Lake Baikal, are common. Wolf is numerous in some places; wood grouse and fox are common; lynx and wolverine are less common. Unique populations of reindeer and black-capped marmot survived in high-mountain belts of ridges on both sides of Lake Baikal thanks to the good protection.
Nerpa (Baikal seal) occupies a special place, being the only representative of the family of pinnipeds on Lake Baikal. Its largest rookery is located on the Malye Ushkanyi Islands.
The goletz complex is characterized by a significantly lower abundance of game animals. Willow and rock ptarmigan, reindeer and ermine belong to permanent residents. This complex can be roughly considered a complementing link to the mountain-taiga one since so many game animals, especially the ungulates, as well as bear, are connected with the highlands by systematic seasonal migrations.
The forest-steppe and steppe complexes stretch in narrow discontinuous bands in the south of the region. They are represented by the Central-Asian mountain steppes and are not distinguished by the abundance of game animals. Only roe deer in the forest-steppe continues to hold the background position among other species, while tarbagan, once numerous in the steppe, has lost its former significance as a result of plowing of the Transbaikalian steppes and its extermination as a carrier of epizootic plague in the course of antiplague measures. Other species characteristic of the forest-steppe zone, namely, badger and raccoon dog, and of the steppe zone, namely, tolai hare, manul, and dzeren, are small in number. Some of them (dzeren and manul) are protected.
The status of game animals is examined only for the Russian part of the Baikal basin. In connection with the reorganizational measures in the Russian hunting sector over the past two decades, some negative manifestations can be noticed in the usage patterns of species valuable for hunting and in the dynamics of their numbers. A number of problems arose, connected mainly with wild ungulates, especially Siberian stag, roe deer, elk, wild reindeer, and in some places musk deer. Concerning these species an undisputed conclusion was made (as, indeed, for other regions) that “the current dynamics of populations of wild ungulates in Russia is determined mainly by hunters (poachers to a greater extent), large predators, and, locally, snowy winters, and not by a natural cyclicity and changes in the productivity of phytocenoses” [Kozhichev, 2002; Danilkin, 2010].
Among large predators the greatest harm is done by wolves. The wolf problem arose due to the loosening of its control. The damage from this predator to the ungulates (Siberian stag and, especially, roe deer) in different regions of Buryatia reaches 8-30% of the autumn herd [Noskov, 2008]. In recent years, in consequence of the irregular decrease in the number of Siberian stag (poaching and death by predators) in conjunction with the legal shooting in Buryatia a crisis situation with the population of this deer was created [Noskov, 2008]. The damage from wolves only in Transbaikalia in 2011 amounted to11.6 million roubles to agriculture and 70-80 million rubles to hunting [Samoilov, Kayukova, 2013]. Because of the large number of wolves in some areas of Transbaikalia an emergency situation was declared [Samoilov, Kayukova, 2013].
In the current situation, the negative effects are smoothed out to some extent through a network of specially protected natural areas. Thus, in Buryatia, 7-8% of the total number of Siberian stag and roe deer are protected within the territories of 13 nature reserves (zakazniks) and 3 reserved areas (zapovedniks) [Noskov, 2008]. Reindeer is listed in the Red Book of the Republic of Buryatia. Measures to protect the hunting grounds, especially in the areas of concentration of animals, are taken.
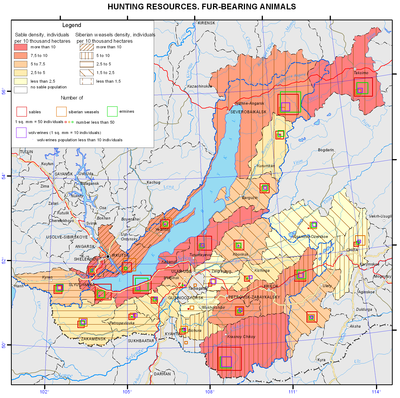
Another situation formed with respect to fur-bearing species of hunting. This is due to the fall in world prices for raw fur. Eighteen million pelts of caged mink from China were mass-marketed [Romanov, 2008]. Because of low prices for Chinese mink, squirrel or muskrat fur coats turned out to be more expensive. As a result, squirrel and muskrat are in little demand on the market. The same situation takes place with other species, namely: fox, Siberian weasel, and ermine. Rare lynx and wolverine pelts are used mainly on the domestic market.
A diametrically opposite situation is with sable enabling Russia to achieve a dominant position in the world market as an exclusive supplier of sable fur. Demand and prices for sable pelts have increased. The price for a sable at an auction averages 220-250 dollars. As opposed to the past years, sable is not endangered as there are less professional hunters. Besides, remote hunting lands are not utilized. They have become a kind of sable reserves, where sables multiply and settle throughout the taiga.
The analysis of the status of hunting fauna in the Baikal basin revealed a number of trends in the features of its use, also characteristic of other regions of the country, in particular, the problem of protecting ungulates. A positive phenomenon is a continued status of sable as the leader in the world fur market, and a removal of the danger of its extermination due to changes in socio-economic conditions, which is important in contrast with previous years.
At the same time, unlike the majority of Siberian regions where a trend of rapid increase in the area of publicly available lands accelerated, in the region under consideration this phenomenon is minimized. This is indicative of targeted optimization of the utilization of game animals resources on the basis of improving forms of hunting management and prospects of its development in the region. Thus, the calculations [Dambiev et al., 2011] made it possible to estimate the socio-economic significance of hunting nature management in the Republic of Buryatia in 2010 as amounting to 1.1 billion roubles. Among them natural products of hunting (furs, meat, etc.) are estimated at 150 million roubles, while the social impact of tourism associated with hunting reaches 450 million roubles. The remaining portion is accounted for by other socio-economic relevance. Therefore, the current state of game fauna in the study region is characterized as conditionally stable. As a result of satisfactory organization of protection of game animals in the region, their number corresponds to a primitive stage of market hunting management.
References
Dambiev, A.G., Kambalin, V.S., and Noskov, V.T. (2011). Hunting nature management of the Republic of Buryatia: problems and prospects. Irkutsk: Izd-vo Irkutskoi selskokhozyaistvennoi akademii. - 109 p.
Danilkin, A. (2010). Wild ungulates of Russia: patterns of population dynamics, in Okhota i okhotnichie khozyaistvo, no.10, pp. 1-4.
Kozhichev, R. (2002). Siberian roe deer in Irkutsk oblast: what to do? in Okhota i okhotnichie khozyaistvo, , no. 12, pp. 4-5.
Noskov, V.T. (2008). Game animals of Buryatia. Ulan-Ude: Izd-vo FGOU VP. “BGSKhA” im. V.V. Filippova, , 223 p.
Romanov, V.I. (2008). Organizational obstacles for producing hunting fur in Eastern Siberia in Protection and sustainable use of animal and plant resources. Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference, May, 29 – June, 1, 2008. Irkutsk: Izd-vo Irkutskoi selskokhozyaistvennoi akademii, pp. 134-136.
Samoilov, E.B. and Kayukova, S.N. (2013). Invasion of wolves in Transbaikalia. Irkutsk: Izd-vo IrGSKhA, pp. 261-263.
Document Actions
Hunting resources. Fur-bearing animals map
Open full size
Game animals
The resource potential of game animals of the Baikal basin has long been characterized by the abundance and high species diversity. This is due to the location of the territory at the intersection of Central-Asian, European-Siberian and East-Asian faunas, where representatives of all of these complexes, including species valuable for hunting, are found. Within the region, there are four typological landscape complexes, corresponding to the zonal and regional landscape subdivisions, namely: mountain-taiga, goletz, forest-steppe, and steppe. Each of them is characterized by a set of habitat types, the quality and quantity of which influence the number of animals.
The wildlife of the mountain taiga is the richest and most diverse; there manifestations of latitudinal zonality in the distribution of vegetation are complicated by the features of altitudinal zonality of its location in the mountains depending on the steepness and exposure of slopes. This creates prerequisites to spread the spectrum of landscape-ecological diversity of the conditions of animal habitats, and possibilities for most of them to choose the most valuable biotopes and, eventually, to increase in the number. In the mountain taiga squirrel, hazel grouse, sable, bear, and in some places musk deer are numerous. Siberian stag and roe deer inhabiting light slopes, forest openings and woodlots, as well as elk, inhabiting waterlogged intermountain depressions, creek valleys and wide plots of terraces in the coastal area of Lake Baikal, are common. Wolf is numerous in some places; wood grouse and fox are common; lynx and wolverine are less common. Unique populations of reindeer and black-capped marmot survived in high-mountain belts of ridges on both sides of Lake Baikal thanks to the good protection.
Nerpa (Baikal seal) occupies a special place, being the only representative of the family of pinnipeds on Lake Baikal. Its largest rookery is located on the Malye Ushkanyi Islands.
The goletz complex is characterized by a significantly lower abundance of game animals. Willow and rock ptarmigan, reindeer and ermine belong to permanent residents. This complex can be roughly considered a complementing link to the mountain-taiga one since so many game animals, especially the ungulates, as well as bear, are connected with the highlands by systematic seasonal migrations.
The forest-steppe and steppe complexes stretch in narrow discontinuous bands in the south of the region. They are represented by the Central-Asian mountain steppes and are not distinguished by the abundance of game animals. Only roe deer in the forest-steppe continues to hold the background position among other species, while tarbagan, once numerous in the steppe, has lost its former significance as a result of plowing of the Transbaikalian steppes and its extermination as a carrier of epizootic plague in the course of antiplague measures. Other species characteristic of the forest-steppe zone, namely, badger and raccoon dog, and of the steppe zone, namely, tolai hare, manul, and dzeren, are small in number. Some of them (dzeren and manul) are protected.
The status of game animals is examined only for the Russian part of the Baikal basin. In connection with the reorganizational measures in the Russian hunting sector over the past two decades, some negative manifestations can be noticed in the usage patterns of species valuable for hunting and in the dynamics of their numbers. A number of problems arose, connected mainly with wild ungulates, especially Siberian stag, roe deer, elk, wild reindeer, and in some places musk deer. Concerning these species an undisputed conclusion was made (as, indeed, for other regions) that “the current dynamics of populations of wild ungulates in Russia is determined mainly by hunters (poachers to a greater extent), large predators, and, locally, snowy winters, and not by a natural cyclicity and changes in the productivity of phytocenoses” [Kozhichev, 2002; Danilkin, 2010].
Among large predators the greatest harm is done by wolves. The wolf problem arose due to the loosening of its control. The damage from this predator to the ungulates (Siberian stag and, especially, roe deer) in different regions of Buryatia reaches 8-30% of the autumn herd [Noskov, 2008]. In recent years, in consequence of the irregular decrease in the number of Siberian stag (poaching and death by predators) in conjunction with the legal shooting in Buryatia a crisis situation with the population of this deer was created [Noskov, 2008]. The damage from wolves only in Transbaikalia in 2011 amounted to11.6 million roubles to agriculture and 70-80 million rubles to hunting [Samoilov, Kayukova, 2013]. Because of the large number of wolves in some areas of Transbaikalia an emergency situation was declared [Samoilov, Kayukova, 2013].
In the current situation, the negative effects are smoothed out to some extent through a network of specially protected natural areas. Thus, in Buryatia, 7-8% of the total number of Siberian stag and roe deer are protected within the territories of 13 nature reserves (zakazniks) and 3 reserved areas (zapovedniks) [Noskov, 2008]. Reindeer is listed in the Red Book of the Republic of Buryatia. Measures to protect the hunting grounds, especially in the areas of concentration of animals, are taken.
Another situation formed with respect to fur-bearing species of hunting. This is due to the fall in world prices for raw fur. Eighteen million pelts of caged mink from China were mass-marketed [Romanov, 2008]. Because of low prices for Chinese mink, squirrel or muskrat fur coats turned out to be more expensive. As a result, squirrel and muskrat are in little demand on the market. The same situation takes place with other species, namely: fox, Siberian weasel, and ermine. Rare lynx and wolverine pelts are used mainly on the domestic market.
A diametrically opposite situation is with sable enabling Russia to achieve a dominant position in the world market as an exclusive supplier of sable fur. Demand and prices for sable pelts have increased. The price for a sable at an auction averages 220-250 dollars. As opposed to the past years, sable is not endangered as there are less professional hunters. Besides, remote hunting lands are not utilized. They have become a kind of sable reserves, where sables multiply and settle throughout the taiga.
The analysis of the status of hunting fauna in the Baikal basin revealed a number of trends in the features of its use, also characteristic of other regions of the country, in particular, the problem of protecting ungulates. A positive phenomenon is a continued status of sable as the leader in the world fur market, and a removal of the danger of its extermination due to changes in socio-economic conditions, which is important in contrast with previous years.
At the same time, unlike the majority of Siberian regions where a trend of rapid increase in the area of publicly available lands accelerated, in the region under consideration this phenomenon is minimized. This is indicative of targeted optimization of the utilization of game animals resources on the basis of improving forms of hunting management and prospects of its development in the region. Thus, the calculations [Dambiev et al., 2011] made it possible to estimate the socio-economic significance of hunting nature management in the Republic of Buryatia in 2010 as amounting to 1.1 billion roubles. Among them natural products of hunting (furs, meat, etc.) are estimated at 150 million roubles, while the social impact of tourism associated with hunting reaches 450 million roubles. The remaining portion is accounted for by other socio-economic relevance. Therefore, the current state of game fauna in the study region is characterized as conditionally stable. As a result of satisfactory organization of protection of game animals in the region, their number corresponds to a primitive stage of market hunting management.
References
Dambiev, A.G., Kambalin, V.S., and Noskov, V.T. (2011). Hunting nature management of the Republic of Buryatia: problems and prospects. Irkutsk: Izd-vo Irkutskoi selskokhozyaistvennoi akademii. - 109 p.
Danilkin, A. (2010). Wild ungulates of Russia: patterns of population dynamics, in Okhota i okhotnichie khozyaistvo, no.10, pp. 1-4.
Kozhichev, R. (2002). Siberian roe deer in Irkutsk oblast: what to do? in Okhota i okhotnichie khozyaistvo, , no. 12, pp. 4-5.
Noskov, V.T. (2008). Game animals of Buryatia. Ulan-Ude: Izd-vo FGOU VP. “BGSKhA” im. V.V. Filippova, , 223 p.
Romanov, V.I. (2008). Organizational obstacles for producing hunting fur in Eastern Siberia in Protection and sustainable use of animal and plant resources. Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference, May, 29 – June, 1, 2008. Irkutsk: Izd-vo Irkutskoi selskokhozyaistvennoi akademii, pp. 134-136.
Samoilov, E.B. and Kayukova, S.N. (2013). Invasion of wolves in Transbaikalia. Irkutsk: Izd-vo IrGSKhA, pp. 261-263.