020. Average annual rainfall in mm map
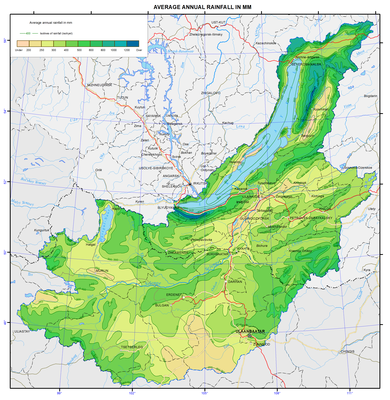
Average annual rainfall in mm map
Mean annual precipitation
Particular features of the mountainous topography have a significant impact on the formation and distribution of precipitation over the study area. The altitude and especially the location of mountains with respect to moisture-laden air flows lead to uneven distribution of precipitation. Different precipitation amount is observed at the same altitudes of mountain ranges. The greatest precipitation amount characterizes the north-western and western slopes of primary (with regard to prevailing air flows) ridges bordering Lake Baikal, i.e. up to 1400 mm; on the windward slopes of secondary ridges and within the plateau inner areas it reaches up to 400-700 mm. Precipitation amount of 200-250 mm fall out in the steppe part of the western shore of Lake Baikal and on its islands, and up to 300 mm precipitate in the intermontane depressions and in the Selenga and Uda river valleys.
Annual precipitation amount of 250-300 mm falls out in the mountains of Khentei at altitudes above 1000 m, in the mountains of the Khovsgol area at altitudes above 1500 m, and in the mountains of Khangai at altitudes above 2000 m. Summer precipitation predominate, constituting 60-70% of the annual amount.