Comfort of available housing (Russian part) map
Urban amenities of the housing fund in
the Russian part of the basin
The share of housing properties with urban amenities is an important factor for ecological well-being of the Baikal basin. Russian statistical data identify the following components of urban amenities: running water, sewage, central heating, hot water supply, baths (showers), and gas and electric stoves. According to the current statistical regulations, all housing properties today are considered to be equipped with central heating irrespectively of the source of heat supply (heat and electric power plant, industrial or local boiler plants, individual boilers). As a rule, the characteristics of the degree of provision with urban amenities is calculated using relative indicators – a percentage of the area of housing properties equipped with the above listed amenities compared to the total area of the housing fund (in %).
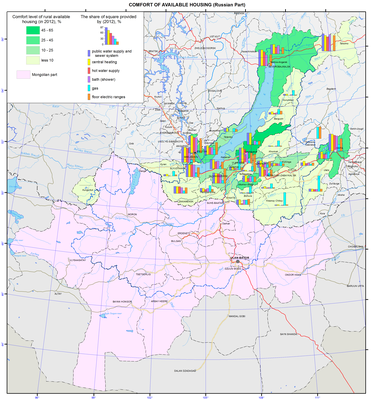
Spatial differences in the comfort level are quite significant in the region. Such regional centres as Irkutsk, Chita, and Ulan-Ude, as well as a town of the republican subordination Severobaikalsk have relatively high levels of urban development. However, a specific share of the housing fund equipped with urban amenities of every second administrative district of the region is less than 25%. Engineering amenities are absent in the Tere-Khol district of Tuva, Yeravna District of Buryatia (except for gas and electric stoves), and Olkhon district of Irkutsk oblast (indicators for running water, heating, gas and electric stoves do not exceed 20%).
The standard indicators of engineering amenities exceed 50% only in every sixth administrative district. The leaders are the Muisky district in Buryatia (due to new housing built during the Baikal-Amur Mainline construction) and Shelekhov and Slyudyanka Districts in the industrial belt surrounding Big Irkutsk (Irkutsk oblast). Almost half of the housing in three more districts has water supply, sewage and central heating: the Severobaikalsk and Kabansk districts in the Republic of Buryatia and the Irkutsk district in Irkutsk oblast.
Rural housing of the region has the lowest indicators of the degree of provision with urban amenities. The map shows the degree of availability of engineering amenities in rural settlements in administrative districts split into four conventionally identified groups according to the first four amenity indicators (i.e., without gas and electric stoves, as it will artificially improve the situation). In every second rural district, less than 10% of housing facilities are equipped with water supply, sewage, central heating, and baths (4th group). In five districts, this indicator is 10-25% (3rd group) (an average level for the region, but two times lower than the average for rural areas of the SFD): the Zaigraevsky, Ivolginsky, Kabansky and Kizhingsky districts in the Republic of Buryatia and Chita district in Zabaikalsky krai. The leader is the Pribaikalsky district of the Republic of Buryatia (1st group: 45-65 %, which is close to the average indicator of the SFD). This district is followed by three other districts with relatively high levels of development of the rural housing fund: the Severobaikalsky and Selenginsky districts in the Republic of Buryatia and the Irkutsk district in Irkutsk oblast (2nd group).
The analysis of indicators of housing development (as of 2012) in the administrative districts of the Russian part of the Baikal basin demonstrates a very low level of modern housing development, high contrasts between urban and rural settlements, and an extremely low level of comfort of rural territories.
References
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Housing and communal services of Zabaikalsky krai. Chita: Zabaikalkraistat. p 112.
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Housing and communal services of the Irkutsk oblast in 2012. Irkutsk: Irkutskstat, 2013. p 76.
Statistical Compendium. (2013). Housing services of the Republic of Buryatia. Ulan-Ude: Buryatstat. p 35.